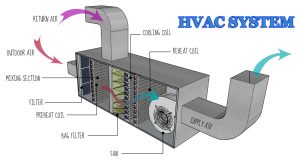
Introduction. A pump is a device that expends energy to raise, transport, or compress fluids—liquids and gases. The term pump is generally used for liquid-handling or hand-operated devices, while the term compressor is used when the pressure of a gas is increased in a motor-driven machine. (See also Pneumatic Device.)
Pumps and compressors are essential mechanical devices used in various industries for fluid transfer and compression purposes. Pumps are primarily used to move liquids or slurries from one place to another by creating a flow through mechanical action. They are commonly used in water supply systems, wastewater treatment plants, and chemical processing facilities. On the other hand, compressors are used to increase the pressure of a gas by reducing its volume. They are vital in applications such as refrigeration, air conditioning, and power generation. Both pumps and compressors play a crucial role in ensuring the efficient operation of industrial processes and systems. Proper maintenance and operation of these machines are essential to prevent breakdowns and ensure optimal performance. Additionally, advancements in technology have led to the development of more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly pump and compressor systems, further enhancing their importance in modern industries.